
Smart Warehousing: How Technology is Revolutionizing Storage
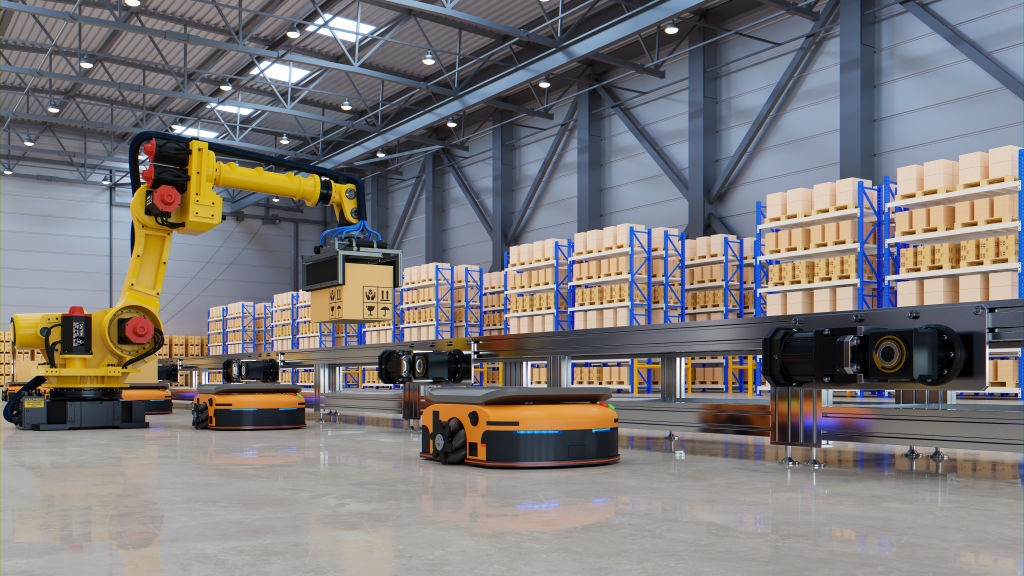

The way we store and move products is changing fast. Gone are the days when warehouses were just big buildings filled with shelves and workers walking around with clipboards. Today’s warehouses are becoming “smart” – using advanced technology to work faster, cheaper, and more accurately than ever before.
What is Smart Warehousing?
Smart warehousing means using modern technology to automate and improve how warehouses operate. Instead of relying only on human workers, these warehouses use computers, robots, and smart systems to handle everything from receiving goods to shipping them out to customers.
Think of it like upgrading from a regular phone to a smartphone – the basic purpose is the same, but the capabilities are dramatically improved.
Key Technologies Transforming Warehouses
1. Robots and Automation
Robots are now common sights in modern warehouses. These aren’t the humanoid robots from science fiction movies, but specialized machines designed for specific tasks:
- Picking robots can grab items from shelves and place them in bins
- Sorting robots organize packages by destination
- Loading robots move heavy items onto trucks
- Inventory robots scan shelves to track what’s in stock
Amazon’s warehouses, for example, use thousands of small robots that look like oversized Roombas to move shelves directly to human workers, saving time and reducing walking.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI acts like the “brain” of smart warehouses. It makes decisions about:
- Which items to store where for fastest access
- The best routes for workers and robots to take
- How much inventory to keep in stock
- When to reorder products before running out
AI can analyze millions of data points in seconds, something that would take humans days or weeks to process.
3. Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors
IoT sensors are tiny devices that monitor everything happening in the warehouse:
- Temperature sensors ensure food and medicine stay fresh
- Motion sensors track how items move through the facility
- Weight sensors verify that packages contain the right products
- Location sensors show exactly where every item is at any moment
These sensors create a real-time picture of warehouse operations, like having thousands of eyes watching everything at once.
4. Automated Storage Systems
Modern warehouses use sophisticated storage systems that work without human intervention:
- Automated shelving that moves items to workers instead of workers going to items
- Vertical storage systems that use every inch of space from floor to ceiling
- Climate-controlled zones that automatically adjust temperature and humidity
- Smart conveyors that sort and route packages automatically
5. Advanced Software Systems
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) coordinate all these technologies:
- Track every item from arrival to shipment
- Optimize storage locations based on demand patterns
- Coordinate robot and human worker schedules
- Integrate with online stores and shipping companies
- Predict future needs based on past data
Real-World Benefits
Faster Operations
Smart warehouses can process orders much faster than traditional ones. What used to take hours now takes minutes. Some facilities can prepare an order for shipping within 15 minutes of receiving it online.
Better Accuracy
Human workers make mistakes – it’s natural. But smart systems are incredibly accurate. Many automated warehouses achieve 99.9% accuracy rates, meaning less than one mistake per thousand orders.
Lower Costs
While the initial investment in technology is high, smart warehouses save money over time through:
- Reduced labor costs
- Less wasted space
- Fewer errors and returns
- Lower energy consumption
- Reduced theft and loss
Improved Safety
Warehouses can be dangerous places with heavy machinery and high shelves. Smart technology makes them safer by:
- Having robots handle the most dangerous tasks
- Using sensors to prevent accidents
- Monitoring air quality and working conditions
- Reducing the need for workers to climb or lift heavy items
Challenges and Considerations
High Initial Costs
Setting up a smart warehouse requires significant upfront investment. The technology, installation, and training can cost millions of dollars, making it challenging for smaller companies to adopt.
Job Changes
Automation does change the nature of warehouse work. While some traditional jobs disappear, new roles emerge:
- Robot technicians who maintain and repair automated systems
- Data analysts who interpret warehouse performance data
- System operators who oversee automated processes
- Quality controllers who ensure everything runs smoothly
Technical Complexity
Smart warehouses are complex systems that require specialized knowledge to operate and maintain. When technology fails, it can shut down operations until experts can fix the problem.
Cybersecurity Risks
Connected systems can be vulnerable to cyber attacks. Warehouses must invest in strong security measures to protect their operations and customer data.
The Future of Smart Warehousing
Drone Deliveries
Some warehouses are testing drones for moving items within the facility and even delivering packages to nearby customers.
Advanced AI
Future AI systems will be even smarter, able to predict customer needs before orders are placed and automatically adjust operations for maximum efficiency.
Sustainable Technology
New technologies focus on reducing environmental impact through:
- Solar-powered facilities
- Electric vehicles for transportation
- Recycling systems for packaging materials
- Energy-efficient lighting and climate control
Integration with Smart Cities
Warehouses will become part of larger smart city networks, coordinating with traffic systems, delivery services, and urban planning to optimize the flow of goods.
Impact on Everyday Life
Smart warehousing directly benefits consumers through:
- Faster delivery times – orders arrive sooner
- Lower prices – efficiency savings are passed to customers
- Better product availability – improved inventory management means fewer out-of-stock situations
- More accurate orders – fewer wrong or damaged items
Getting Started with Smart Warehousing
For businesses considering smart warehousing technology:
Start Small
Begin with one or two technologies rather than trying to automate everything at once. Many companies start with inventory management software or basic automation systems.
Assess Your Needs
Consider your specific challenges. Do you need faster processing, better accuracy, or reduced costs? Different technologies address different problems.
Plan for Training
Invest in training your workforce to work alongside new technologies. The most successful smart warehouses combine human intelligence with machine efficiency.
Partner with Experts
Work with technology providers who understand warehousing operations and can provide ongoing support.
Conclusion
Smart warehousing represents a fundamental shift in how we store and distribute products. While the technology can seem complex, the basic goal is simple: get the right products to the right people faster, cheaper, and more accurately than ever before.
This transformation is still in its early stages. As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, smart warehousing will become accessible to more businesses, ultimately benefiting everyone through better service and lower prices.
The future of storage isn’t just about building bigger warehouses – it’s about building smarter ones. And that future is arriving faster than many people realize.















Post Comment