
PDCA Cycle: A Practical Guide to Continuous Improvement
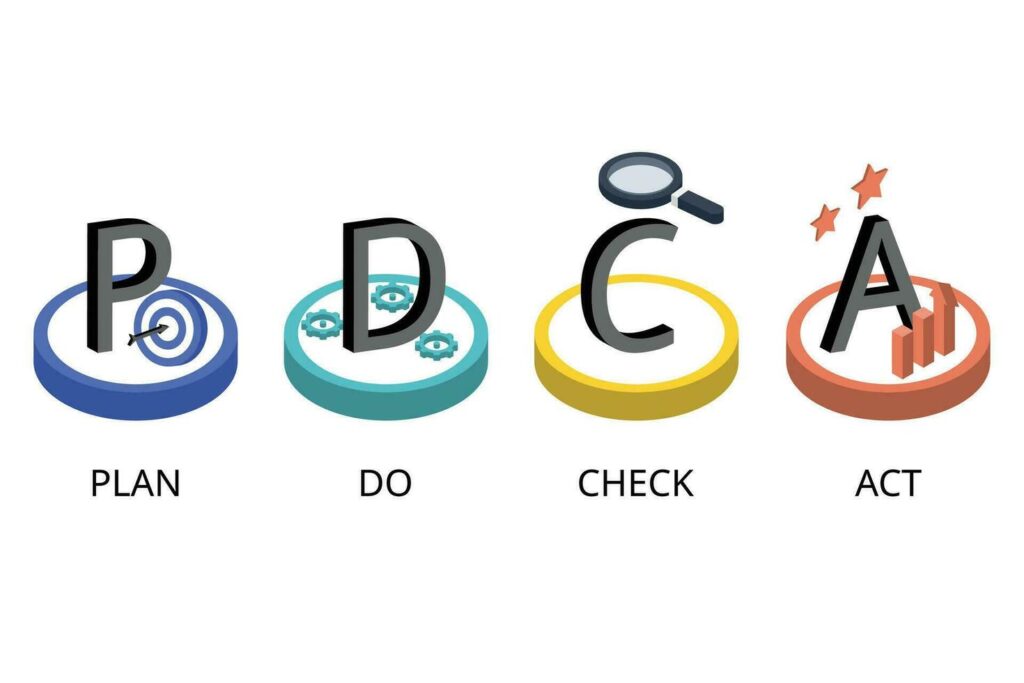
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle represents a cornerstone methodology for organizations pursuing operational excellence and sustainable competitive advantage. This systematic approach to continuous improvement has transformed countless enterprises across industries, delivering measurable results through structured problem-solving and process optimization.
Understanding PDCA: Foundation of Continuous Improvement
Defining the PDCA framework – The PDCA cycle, originally developed by Dr. W. Edwards Deming, provides a robust foundation for systematic improvement initiatives. This iterative methodology encompasses four distinct phases: strategic planning, controlled implementation, performance analysis, and standardization or revision. Organizations worldwide leverage this framework to drive innovation, enhance quality, and optimize operational efficiency.
Strategic value proposition – Modern enterprises face unprecedented challenges requiring agile response mechanisms and data-driven decision-making processes. The PDCA methodology addresses these needs by providing a structured approach that minimizes risk exposure while maximizing learning opportunities. Companies utilizing this framework report significant improvements in process efficiency, customer satisfaction, and employee engagement.
Phase 1: Plan – Strategic Analysis and Solution Design
Root Cause Analysis and Problem Definition
Effective PDCA implementation begins with comprehensive problem identification and analysis. Organizations must move beyond symptom management to identify underlying systemic issues that impact performance. This requires sophisticated analytical techniques including fishbone diagrams, 5-why analysis, and statistical process control methods.
Data-driven problem assessment involves collecting quantitative metrics, conducting stakeholder interviews, and analyzing performance trends. Leading organizations invest in robust data analytics capabilities to support this phase, ensuring decisions are based on empirical evidence rather than assumptions or intuition.
Objective Setting and Success Metrics
Strategic planning requires the establishment of specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives. These targets must align with broader organizational goals while addressing identified performance gaps. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established to enable accurate measurement of improvement initiatives.
Performance measurement frameworks typically include leading indicators (predictive metrics), lagging indicators (outcome measures), and operational metrics (process efficiency measures). This comprehensive approach ensures organizations can track progress throughout the improvement cycle and make data-informed adjustments as needed.
Solution Architecture and Resource Allocation
Developing effective solutions requires cross-functional collaboration, stakeholder engagement, and strategic resource allocation. Organizations must evaluate multiple alternatives, assess implementation feasibility, and design pilot programs that minimize disruption while maximizing learning potential.
Change management considerations include communication strategies, training requirements, technology needs, and organizational readiness assessments. Successful PDCA implementations integrate these elements into comprehensive project plans that address both technical and human factors.
Phase 2: Do – Controlled Implementation and Pilot Execution
Pilot Program Design and Execution
The implementation phase focuses on controlled experimentation through carefully designed pilot programs. These initiatives should be limited in scope, duration, and resource requirements to minimize risk while generating actionable insights. Best practices include selecting representative test environments, defining clear boundaries, and establishing rigorous monitoring protocols.
Pilot program management requires dedicated project teams, clear communication channels, and robust documentation processes. Organizations should implement daily huddles, weekly progress reviews, and milestone assessments to ensure pilots remain on track and deliver expected outcomes.
Data Collection and Documentation Standards
Comprehensive data collection during the implementation phase provides the foundation for subsequent analysis and decision-making. Organizations must establish standardized documentation procedures, data quality controls, and real-time monitoring systems to capture relevant information throughout the pilot period.
Documentation requirements include process observations, performance measurements, stakeholder feedback, unexpected events, and resource utilization data. Advanced organizations leverage digital platforms and automation tools to streamline data collection while ensuring accuracy and completeness.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Effective PDCA implementation requires proactive risk management and contingency planning. Organizations must identify potential failure modes, develop mitigation strategies, and establish escalation procedures to address unexpected challenges during pilot execution.
Risk mitigation strategies include regular checkpoint reviews, stakeholder communication protocols, and predefined rollback procedures. These measures ensure organizations can respond quickly to emerging issues while protecting operational continuity and stakeholder confidence.
Phase 3: Check – Performance Analysis and Results Evaluation
Statistical Analysis and Performance Assessment
The analysis phase transforms raw data into actionable insights through statistical analysis, trend identification, and comparative assessment. Organizations must employ appropriate analytical techniques to evaluate pilot performance against established success criteria and identify factors contributing to outcomes.
Advanced analytics capabilities include regression analysis, control charts, hypothesis testing, and predictive modeling. These tools enable organizations to understand not just what happened, but why it happened and what might happen under different conditions.
Stakeholder Feedback and Qualitative Assessment
Quantitative analysis must be complemented by qualitative feedback from stakeholders, including employees, customers, and process owners. This input provides context for numerical results and identifies factors that may not be captured through traditional metrics.
Feedback collection methods include structured interviews, focus groups, surveys, and observational studies. Organizations should design these activities to capture honest, unbiased input that reflects actual stakeholder experiences during the pilot period.
Gap Analysis and Performance Benchmarking
Comprehensive evaluation requires comparing actual results against planned objectives, industry benchmarks, and best practice standards. This analysis identifies performance gaps, improvement opportunities, and areas requiring additional attention in subsequent cycles.
Benchmarking strategies involve internal comparisons (against historical performance), competitive analysis (against industry peers), and functional benchmarking (against best-in-class organizations regardless of industry). These perspectives provide comprehensive context for performance evaluation.
Phase 4: Act – Strategic Decision-Making and Standardization
Implementation Decision Framework
The final phase requires strategic decisions regarding pilot outcomes and future actions. Organizations must evaluate results objectively, considering both quantitative performance and qualitative factors, to determine optimal next steps.
Decision criteria typically include achievement of success metrics, stakeholder satisfaction levels, resource requirements, implementation complexity, and alignment with strategic objectives. This multi-dimensional assessment ensures decisions support long-term organizational success.
Process Standardization and Knowledge Transfer
Successful pilots require systematic standardization to ensure consistent implementation across the organization. This involves developing standard operating procedures, training programs, and quality assurance mechanisms that preserve improvement gains while enabling scalable deployment.
Knowledge management systems capture lessons learned, best practices, and implementation guidelines to support future improvement initiatives. Organizations should establish repositories, communities of practice, and mentoring programs to facilitate knowledge transfer and capability development.
Continuous Improvement Culture Development
PDCA implementation success depends on establishing a culture that values continuous improvement, experimentation, and learning. Organizations must invest in change management, employee development, and recognition systems that reinforce desired behaviors and attitudes.
Cultural transformation strategies include leadership development, employee empowerment initiatives, innovation programs, and performance management systems aligned with continuous improvement principles. These elements create sustainable organizational capabilities that support long-term excellence.
Industry Applications and Success Stories
Manufacturing Excellence
Manufacturing organizations have leveraged PDCA principles to achieve significant improvements in quality, efficiency, and cost performance. Leading companies report defect reductions of 50-90%, cycle time improvements of 20-40%, and cost savings of 10-25% through systematic PDCA implementation.
Toyota Production System exemplifies world-class PDCA application, incorporating continuous improvement (kaizen) principles throughout operations. Their approach demonstrates how systematic problem-solving and employee engagement can deliver sustained competitive advantage.
Healthcare Quality Improvement
Healthcare organizations utilize PDCA methodology to enhance patient safety, clinical outcomes, and operational efficiency. Successful implementations have reduced medical errors by 30-60%, improved patient satisfaction scores by 15-30%, and decreased readmission rates by 10-20%.
Institute for Healthcare Improvement promotes PDCA-based improvement methodologies that have transformed healthcare delivery across thousands of organizations worldwide. Their Model for Improvement integrates PDCA principles with healthcare-specific quality frameworks.
Service Industry Transformation
Service organizations apply PDCA principles to improve customer experience, operational efficiency, and employee productivity. Results include customer satisfaction improvements of 20-40%, service delivery time reductions of 25-50%, and employee engagement increases of 15-30%.
Hospitality and financial services sectors demonstrate particularly strong PDCA adoption, with leading organizations achieving industry recognition for service excellence through systematic improvement initiatives.
Advanced PDCA Integration Strategies
Technology-Enabled PDCA Implementation
Digital transformation enables more sophisticated PDCA implementation through automation, real-time analytics, and artificial intelligence capabilities. Organizations leverage these technologies to accelerate cycle times, improve data quality, and enhance decision-making effectiveness.
Digital platforms support collaborative planning, automated data collection, advanced analytics, and standardized documentation. These capabilities enable organizations to conduct more experiments, analyze results more quickly, and implement improvements more effectively.
Enterprise-Wide PDCA Deployment
Mature organizations implement PDCA principles across all functions and levels, creating integrated improvement networks that drive systematic organizational advancement. This requires sophisticated governance structures, communication systems, and performance management frameworks.
Scaling strategies include executive sponsorship, dedicated improvement resources, cross-functional teams, and integrated performance metrics. Successful enterprise deployments typically require 2-3 years to achieve full maturity and begin delivering maximum value.
Strategic Alignment and Portfolio Management
Advanced PDCA implementation aligns improvement initiatives with strategic objectives through portfolio management approaches that prioritize projects, allocate resources, and coordinate interdependent activities.
Portfolio management frameworks evaluate improvement opportunities based on strategic impact, resource requirements, implementation complexity, and expected returns. This ensures organizations focus on highest-value initiatives while maintaining balanced improvement portfolios.
Implementation Roadmap and Best Practices
Phase 1: Foundation Building (Months 1-3)
Successful PDCA implementation begins with foundation building activities including leadership alignment, capability assessment, and pilot selection. Organizations should invest in training, communication, and infrastructure development to support subsequent phases.
Critical success factors include executive sponsorship, dedicated resources, clear objectives, and realistic timelines. Organizations should resist the temptation to implement too quickly or across too broad a scope initially.
Phase 2: Pilot Execution (Months 4-9)
The pilot phase focuses on controlled experimentation with selected improvement opportunities. Organizations should emphasize learning over results, maintaining rigorous documentation and analysis standards throughout the pilot period.
Pilot management best practices include regular progress reviews, stakeholder communication, problem escalation procedures, and knowledge capture systems. These elements ensure pilots generate maximum learning while minimizing organizational disruption.
Phase 3: Expansion and Integration (Months 10-18)
Successful pilots provide the foundation for broader implementation across additional functions, processes, and organizational levels. This phase requires careful change management, resource scaling, and performance monitoring to ensure consistent results.
Expansion strategies should balance speed with quality, ensuring adequate support systems exist before implementing improvements in new areas. Organizations must maintain momentum while avoiding implementation fatigue or quality degradation.
Phase 4: Maturity and Optimization (Months 19+)
Mature PDCA implementations focus on optimization, innovation, and strategic integration. Organizations should continuously evaluate methodology effectiveness, incorporate new techniques, and align improvement activities with evolving strategic priorities.
Optimization opportunities include advanced analytics, automation technologies, cross-industry benchmarking, and integrated performance management systems. These capabilities enable organizations to achieve world-class improvement performance and sustainable competitive advantage.
Measuring PDCA Implementation Success
Key Performance Indicators
Effective PDCA measurement requires balanced scorecards that capture multiple dimensions of improvement performance. Organizations should track leading indicators (improvement activities), process indicators (cycle effectiveness), and lagging indicators (business results).
Essential metrics include improvement project completion rates, cycle time reduction, employee participation levels, customer satisfaction improvements, and financial impact measures. These indicators provide comprehensive visibility into PDCA implementation effectiveness.
Return on Investment Analysis
Organizations must quantify PDCA implementation value through rigorous return on investment (ROI) analysis. This includes direct cost savings, revenue improvements, productivity gains, and risk reduction benefits.
ROI calculation methodologies should account for implementation costs, ongoing operational expenses, and both tangible and intangible benefits. Leading organizations typically achieve 300-500% ROI within 18-24 months of full implementation.
Capability Maturity Assessment
Long-term PDCA success requires continuous assessment of organizational improvement capabilities. Maturity models provide frameworks for evaluating current state, identifying development priorities, and tracking capability advancement over time.
Maturity dimensions include leadership commitment, employee engagement, process standardization, data analytics capabilities, and cultural transformation. Organizations should conduct annual assessments to guide improvement strategy development and resource allocation decisions.
Future Trends and Evolution
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Emerging technologies are transforming PDCA implementation through artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive analytics capabilities. These tools enable more sophisticated problem identification, solution optimization, and outcome prediction.
AI applications include automated root cause analysis, predictive failure detection, optimization algorithm development, and intelligent decision support systems. Organizations investing in these capabilities gain significant competitive advantages in improvement speed and effectiveness.
Sustainable Development Integration
Modern PDCA implementation increasingly incorporates sustainability considerations, environmental impact assessment, and social responsibility factors. This evolution reflects growing stakeholder expectations and regulatory requirements.
Sustainability frameworks integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into improvement decision-making processes. Organizations adopting these approaches demonstrate leadership in corporate responsibility while achieving superior business performance.
The future of PDCA lies in its continued evolution as a comprehensive framework for organizational excellence, integrating new technologies, stakeholder expectations, and strategic imperatives. Organizations mastering this methodology position themselves for sustained success in increasingly competitive and dynamic business environments.
Implementing PDCA represents a strategic investment in organizational capability development, competitive advantage creation, and sustainable performance improvement. Companies committed to excellence recognize this methodology as essential for thriving in tomorrow’s business landscape.















Post Comment